Planning catalogs or multi product offers.
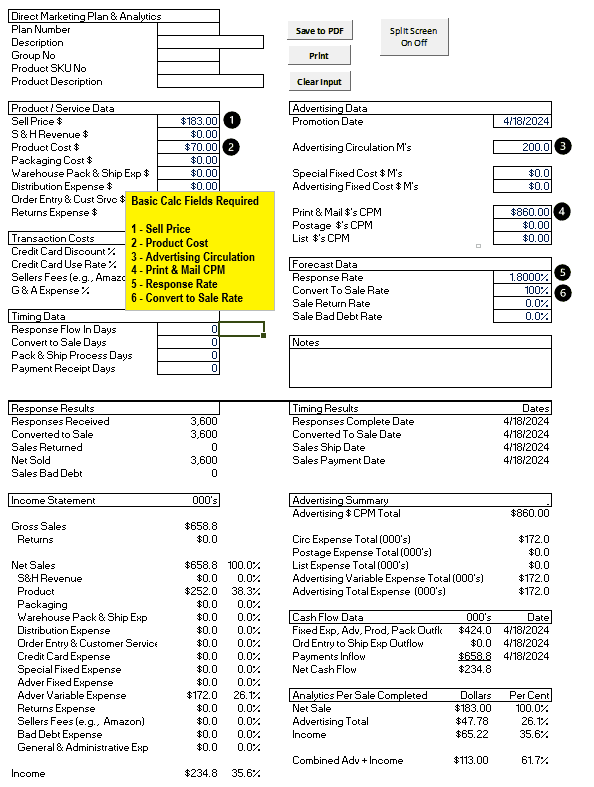
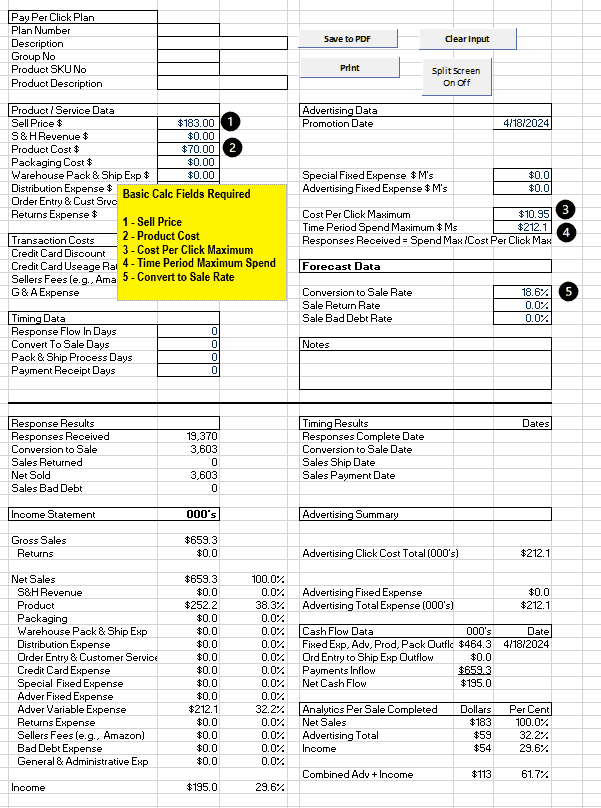
MPP Single templates only use one input for Product Sell Price and Cost. (Other product related inputs are Packaging (that holds the product and can be fancy or plain), Warehousing-Packing-Shipping, and Distribution (UPS, Fedex, USPS).
The approach to use for multi-product offers – or catalogs is as follows:
Analyze Previous Sales
Analyze sales with a view towards the 80/20 theory to identify best sellers. The 80/20 theory, also known as the Pareto principle, states that for many outcomes, roughly 80% of consequences come from 20% of causes. This theory can be applied to a wide range of things, including sales of catalogs or multi product offers.
In the context of selecting the best sellers for a catalog, the 80/20 theory suggests that 80% of sales will come from 20% of the products. This assumes that the products all get equal weight in terms of advertising, promotion and focus.
To apply the 80/20 theory to selecting the best sellers in a catalog using only internal historical data, especially price and sorting into different quintiles, you can follow these steps:
Identity Best Sellng and Outlier Products
Identify your top-selling items. Rank your products by sales volume over the past year or two. Take into account the advertising expense focused on each and include the advertising to sales ratio (Advertising/Sales) to weight the sales.
Create quintile group segments of the products by sales. With the lowest sales quintile numbered 1 and highest numbered 5, middle groups 2, 3 and 4 in between.
Consider not including products that are outliers with either very high prices or low prices that will skew the averages. An example would be a product with a price of $200 and all the other products in the quintile are $20 to $50.
Create Plans for Each Group
Create a single plan for each group using the average sell price, product cost and other non-advertising key drivers. Then apply the advertising key drivers for direct marketing or pay per click. This may show the different margins available for advertising expense and very different response requirements for profitable campaigns. In other words, if the top quintile (number 5) group also has higher average sell price and gross margins, this will allow for more margin for advertising and “order acquisition” at lower response rates or lower cost per click.
After evaluating the groups on an average, then load each group into a Multi template. Multi calculates each of up to 15 different groups as stand-alone and then summarizes the combined financial results for all groups.
The Groups template does something similar for from 3 to 199 groups. But for working with quintiles, Multi is just fine.